Computer Networks:
- Types of network (LAN MAN WAN)
- Network Topologies
- Transmission Techniques (simplex, 1/2 duplex, duplex)
- Physical Media(Guided /unguided)
- Hub, Repeater,
- Functions of DLL
- Sub-Layer (LLC & MAC Address)
- Error Detection(Parity check & Checksum)
- Correction Technique(Hamming Code)
- Concept of Switch.
- Switching Technique (CS,MS,PS)
Network Layer
- Function of Network Layer
- Addressing
- IP Addressing(Class A,B,C,D,E)
- IPv4 Packet Format
- Basic of Routing Protocol ARP,RARP.
- Sub-netting
- Concept of IPv6
- IPv4 Vs IPv6
- Router
Transport Layer:
- Function of Transport Layer
- Transport Layer Protocols TCP,UDP
- Multiplexing and Demultiplexing
- Congestion Control
- Flow Control
Session and Presentation Layer:
Application Layer:
- function of Application Layer
- Application Layer Protocol HTTP
- TFTP, SMTP, POP, URL
- FTP
- TELNET.
- concept of Gateway.
- DNS
- MIME
- WWW
- E-mail, IMAP
What is Network Topologies
Network Topologies:
Physical topology or network topology refers to the configuration of cables computers and other peripheral devices.
Network topologies tell us about how a system or a network is interconnected with each other.
The main types of physical topologies are:
- Point to point
- Bus topology
- Star topology
- Ring Topology
- Mesh topology
Point to Point:

In point-to-point topology, the two systems are connected directly with each other.
Bus Topology:
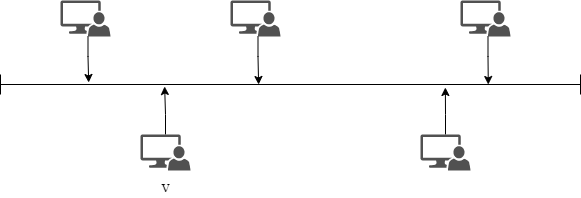
In bus topology, all the systems are connected on a single cable.
Advantages of bus topology:
- Easier to o connect a system
- Less cables required.
Disadvantages of bus topology:
- If there is a break in the main cable all the system will be closed
- Difficult to identify the problems.
Star topology:
In star topology, all systems are directly connected to a central network hub switch.
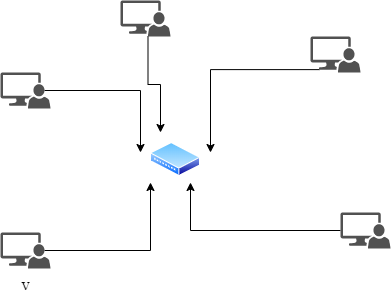
Advantages of star topology:
- Easier to install
- Easy to add new network
- If one system fails rest will work.
Disadvantages of Star topology:
- Required more cable than a linear topology.
- If the switch or hub disable all network will be closed.
- Expensive than linear bus topology
Tree Topology:
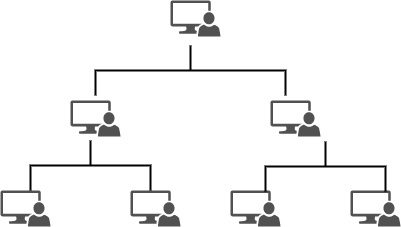
Tree topology is a combination of bus and star topology. Tree topology tree-like structure.
Advantages of Tree topology:
- Point-to-point wiring for individual system
- has several hardware and software support
Disadvantages of Tree topology:
- If the backbone line breaks the entire system goes down
- Difficult to Configure.
Mesh Topology:
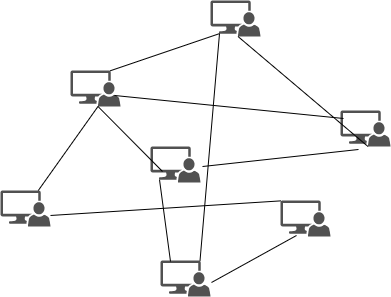
- In mesh topology the systems are connected independently with other systems.
- Mesh topology message sent to the destination can take any possible shortest easier route to reach its destination.
Advantages of Mesh topology:
- Provide a path between two devices
- The network can be extended without disturbing current users
Disadvantages of Mesh topology:
- Cost is higher
- Structuring and the maintenance are also expensive and complex
Things to consider when choosing topologies:
while choosing topology several things should consider before choosing a topology. There are many things to look at before choosing auto topology some of main things are:
Money:
The first thing is Money, we should keep in mind the expenditure before and after. financial support is required so while choosing a topology we must see the cost.
Length of the cable needed:
Is the length of the cable required before and after the system is applied, increase wire length mean expensive may increase?
Future growth:
While choosing a topology we must put our future expansion policy to increase our system to a limited extent.
Cable type:
The most common cable in school is unshielded twisted pair which is most often used in Star topologies, so wire types is also the most important thing to be look for.
Computer Networks:
- Types of network (LAN MAN WAN)
- Network Topologies
- Transmission Techniques (simplex, 1/2 duplex, duplex)
- Physical Media(Guided /unguided)
- Hub, Repeater,
- Functions of DLL
- Sub-Layer (LLC & MAC Address)
- Error Detection(Parity check & Checksum)
- Correction Technique(Hamming Code)
- Concept of Switch.
- Switching Technique (CS,MS,PS)
Network Layer
- Function of Network Layer
- Addressing
- IP Addressing(Class A,B,C,D,E)
- IPv4 Packet Format
- Basic of Routing Protocol ARP,RARP.
- Sub-netting
- Concept of IPv6
- IPv4 Vs IPv6
- Router
Transport Layer:
- Function of Transport Layer
- Transport Layer Protocols TCP,UDP
- Multiplexing and Demultiplexing
- Congestion Control
- Flow Control
Session and Presentation Layer:
Application Layer:
- function of Application Layer
- Application Layer Protocol HTTP
- TFTP, SMTP, POP, URL
- FTP
- TELNET.
- concept of Gateway.
- DNS
- MIME
- WWW
- E-mail, IMAP