Computer Networks:
- Types of network (LAN MAN WAN)
- Network Topologies
- Transmission Techniques (simplex, 1/2 duplex, duplex)
- Physical Media(Guided /unguided)
- Hub, Repeater,
- Functions of DLL
- Sub-Layer (LLC & MAC Address)
- Error Detection(Parity check & Checksum)
- Correction Technique(Hamming Code)
- Concept of Switch.
- Switching Technique (CS,MS,PS)
Network Layer
- Function of Network Layer
- Addressing
- IP Addressing(Class A,B,C,D,E)
- IPv4 Packet Format
- Basic of Routing Protocol ARP,RARP.
- Sub-netting
- Concept of IPv6
- IPv4 Vs IPv6
- Router
Transport Layer:
- Function of Transport Layer
- Transport Layer Protocols TCP,UDP
- Multiplexing and Demultiplexing
- Congestion Control
- Flow Control
Session and Presentation Layer:
Application Layer:
- function of Application Layer
- Application Layer Protocol HTTP
- TFTP, SMTP, POP, URL
- FTP
- TELNET.
- concept of Gateway.
- DNS
- MIME
- WWW
- E-mail, IMAP
Network Switching Technique
Switching
For transmission of data beyond local area, communication is achieved by transmitting data from source to destination through a network of intermediate node, this node are called switching nodes, the method of transmitting data is called switching.
The switching technique will choose the best route for data transmission.
There are three types of switching techniques:
- Circuit switch
- Message switch
- Packet switch

1) Circuit Switching:
In the circuit switching technique, first the physical connection between two computer is established and then data transmitted from the source computer to the destination computer.(therefore it is also called dedicated)
In circuit switching once connection is established then the dedicated path will remains to exist until the connection is terminated.

Advantages of circuit switching:
- The circuit is very simple.
- Once the circuit is established the network is effectively transparent to user.
- The delay at each not is negligible.
- Information is transmitted at a fixed data rate.
Disadvantages of circuit switching:
- Circuit switching is in effective.
- channel capacity is not properly utilized.
- There is a delay prior to signal transfer or call establish.
- Less flexible as It is dedicated bath.
- It is suitable for voice communication but not for data communication.
2) Message switching :
In this message technique, the source computer sends data or the message to the switching office(Node) fast, which stores the data in its buffer, then look for a free link to another switch office (Node) and then send the data to the office this process is continue until the data deliver to the destination computer. it is otherwise called store and forward.

Advantages of message switching:
- No propagation delay.
- Channel is properly utilize.
Disadvantages of message switching:
- The delay is here at each not.
- Requirement of last capacity storage mediate is not.
3) Packet switching:
In packet switching the message send in one go but it divides into small pieces packet individual
Into small pieces known as packets.
Each packet content source address and destination address and sequence number.
Packet will be travel across the network taking shortest path as possible, and packets Reassemble at receiver side according to sequence.
There are two approaches in this switching technique:
- Datagram approach
- Virtual circuit approach
3.a)Datagram Approach:
in this approach no dedicated part is established and all the package belongs to the same message needs not go by one route to reach the destination. Packets can go from different part to reach Destination. there order of reaching destination may be different then starting order.

Advantages of datagram:
- The call set up phase is avoid it.
- Is more flexible more reliable
Disadvantages of datagram:
- The order of reaching is not same as the starting order so The Lost of packet cannot be seen.
- For longer and large packet it is not suitable.
3.b) Virtual circuit approach:
the relationship between all the packet belongs to the same message is preserve a single root is chosen between Sender and receiver.
Two format of virtual circuit transmission:
- (SVC) switched virtual circuit.
- (PVC) permanent virtual circuit
switch virtual circuit (SVC)
in this virtual circuit is created when ever it is need to exists only for the duration of the specific exchange.
Permanent Virtual Circuit(PVC):
In this, Same Virtual circuit is provided between two user on a continuous basis, the circuit is dedicated for specific use and no one else can use it.
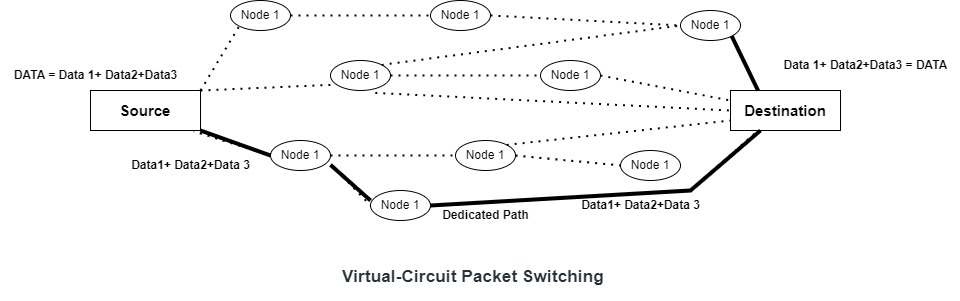
Advantages of virtual Circuit:
- no need of routing decision.
- it provide sequence.
- package should transmit more Rapid with a virtual circuit.
Disadvantages of virtual circuit:
- if node fails all virtual circuit that passes through the nodes are lost.
- Packet fallow a pre define root it is more difficult to Adapt to congestion
Computer Networks:
- Types of network (LAN MAN WAN)
- Network Topologies
- Transmission Techniques (simplex, 1/2 duplex, duplex)
- Physical Media(Guided /unguided)
- Hub, Repeater,
- Functions of DLL
- Sub-Layer (LLC & MAC Address)
- Error Detection(Parity check & Checksum)
- Correction Technique(Hamming Code)
- Concept of Switch.
- Switching Technique (CS,MS,PS)
Network Layer
- Function of Network Layer
- Addressing
- IP Addressing(Class A,B,C,D,E)
- IPv4 Packet Format
- Basic of Routing Protocol ARP,RARP.
- Sub-netting
- Concept of IPv6
- IPv4 Vs IPv6
- Router
Transport Layer:
- Function of Transport Layer
- Transport Layer Protocols TCP,UDP
- Multiplexing and Demultiplexing
- Congestion Control
- Flow Control
Session and Presentation Layer:
Application Layer:
- function of Application Layer
- Application Layer Protocol HTTP
- TFTP, SMTP, POP, URL
- FTP
- TELNET.
- concept of Gateway.
- DNS
- MIME
- WWW
- E-mail, IMAP